This is what I learned from App Router: Adding Search and Pagination | Next.js. I believe the diagrams greatly helped me understand the framework.
🔭Overview
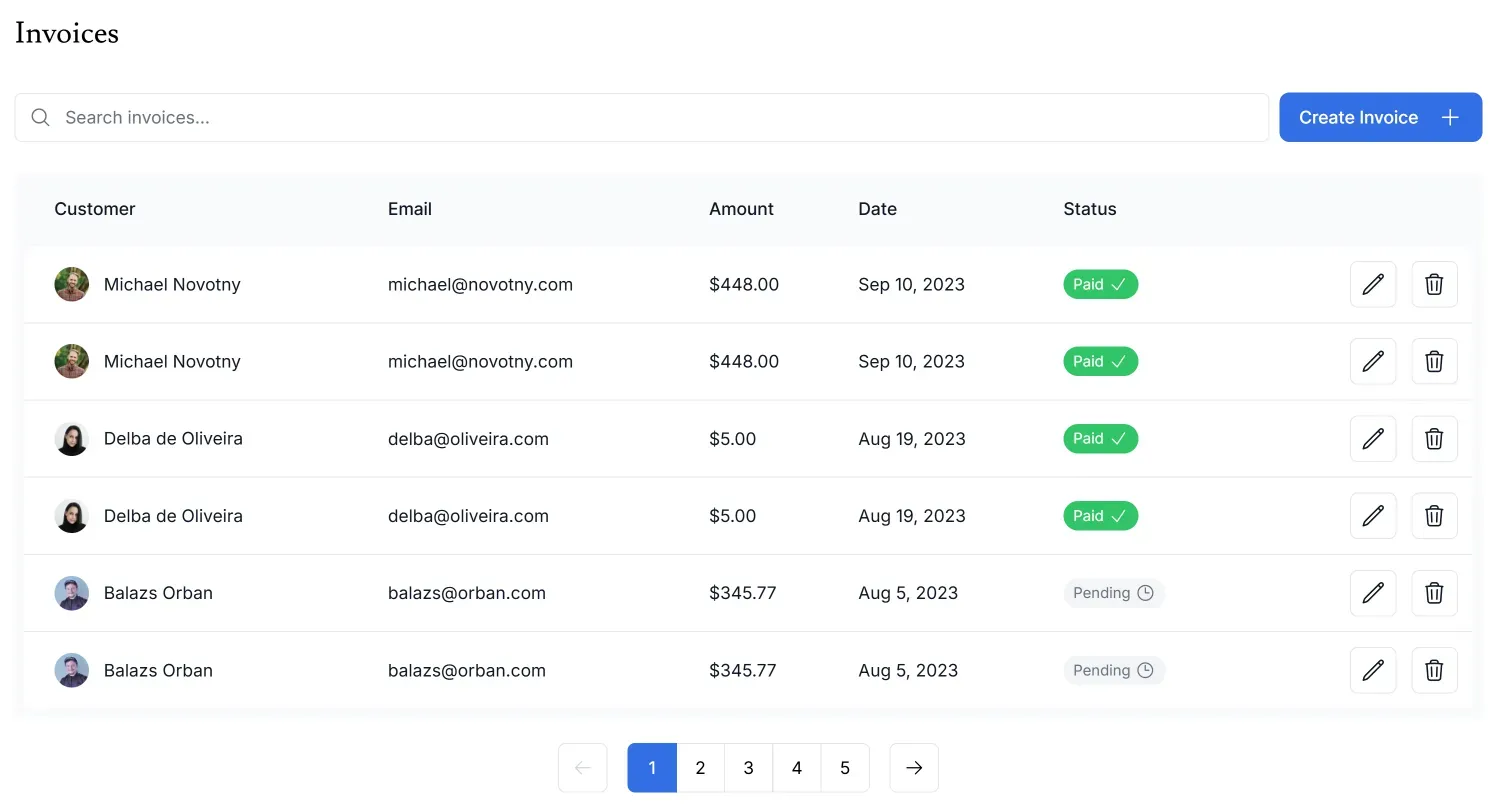
In short, the function described here is to search for an invoice in the database and display it in a table. The pattern uses URL search parameters, meaning that when you search, the URL will look like /dashboard/invoices?page=1&query=pending. This approach is beneficial for SEO and bookmarking.
🧪UI Composition
The UI layout could be simplified like so:
<Page>
<Search />
<Table />
<Pagination />
</Page>
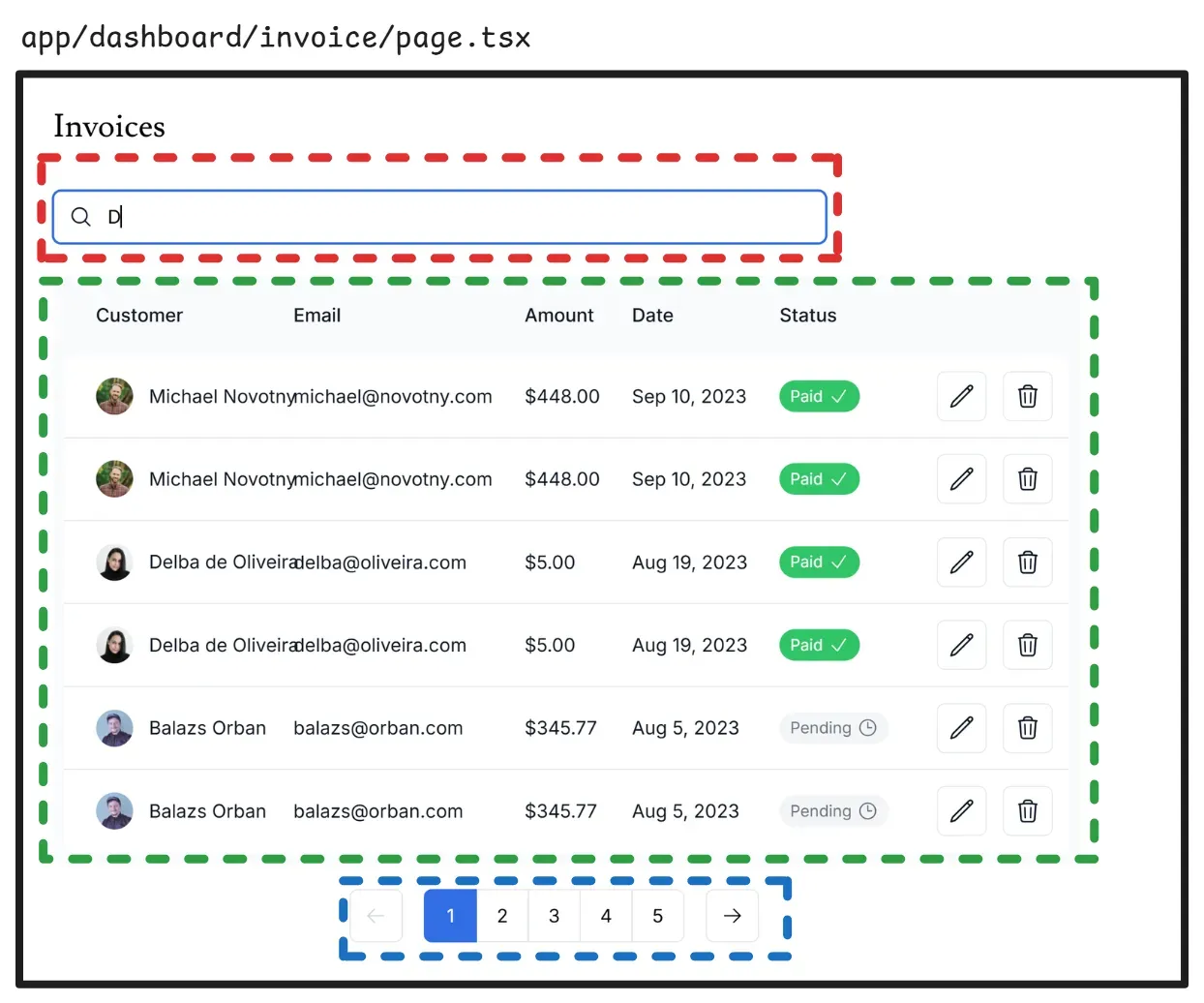
- 🟥: search (client component)
- 🟩: table (server component)
- 🟦: pagination (client component)
✏️Workflow
Let me give you a big picture of how each .tsx affect the URL.
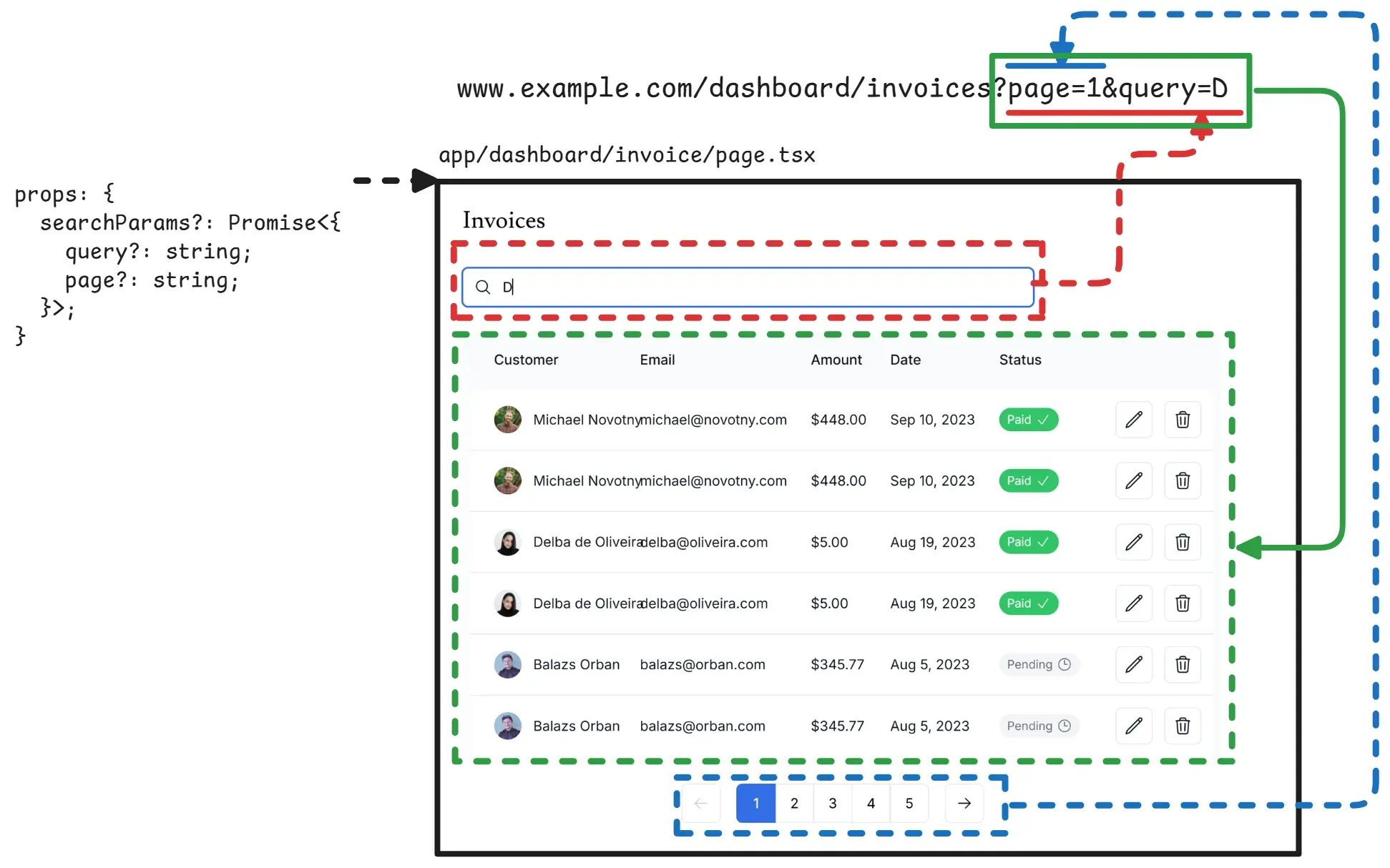
0️⃣ url
Since 🟥🟩🟦 are all composed inside the <Page />, when we use usePathname() to get the current URL, it always return the www.example.com/dashboard/invoice.
1️⃣ search
Whenever the user initiates a search, the text is parsed by the <Search/> component. For example, if I type “D” and the <Search/> component will updates the URL to /dashboard/invoices?page=1&query=D using the next.js function useRouter().(see the red arrow)
2️⃣ navigate
How does the navigation component know the number of pages?
Great question! The
<Pagination />is a client component and we don’t want to expose the database secrets to it, as that would be dangerous!
The solution is to calculate the number of pages in the<Page />component (a server component) and pass the value to the<Pagination />.
When user click the ⬅️ or ➡️, the <Pagination /> updates the page in the search parameters(see the blue arrow).
3️⃣ the Page
export default async function Page(props: {
searchParams?: Promise<{
query?: string;
page?: string;
}>;
}) {
const searchParams = await props.searchParams;
const query = searchParams?.query || '';
const currentPage = Number(searchParams?.page) || 1;
const totalPages = await fetchInvoicesPages(query);
return (
<div>
<Search placeholder="Search invoices..." />
<Table query={query} currentPage={currentPage} />
<Pagination totalPages={totalPages} />
</div>
);
}Whenever the <Search /> or <Pagination /> changes the URL, the <Page/> parses the searchParams. The query and page values are then passed to the <Table /> to display.
4️⃣ table
Finally, the <Table /> is responsible for displaying the data.